As the pipeline of drugs for diabetes management continues to grow, benefit partners and advisors and the employer groups they serve are positioned to influence significant decisions that will impact healthcare spending. With some groups spending millions for diabetic drugs alone, it’s critical to understand the full spectrum of medications available, including newer players like Jardiance, Trulicity, Januvia, Farxiga and established treatments like Metformin and insulins, to ensure both the cost-effective and clinically effective management of diabetes.
Comprehensive Overview of Diabetic Drug Classes
- Biguanides (e.g., Metformin): Metformin, a cornerstone in diabetes treatment, is known for its efficacy in lowering blood glucose without causing weight gain or significant hypoglycemia. It is particularly noted for some cardiovascular benefits and is affordable due to its generic availability. However, it may be unsuitable for patients with severe renal impairment and can cause gastrointestinal side effects.
- SGLT2 Inhibitors (e.g., Jardiance, Farxiga): These drugs not only control blood glucose effectively but also offer additional benefits such as intermediate weight loss and significant cardiovascular and renal advantages, making them ideal for patients with comorbid conditions. The availability of generics for drugs like Farxiga presents an opportunity for cost savings.
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonists (e.g., Trulicity, Ozempic): Known for their potent impact on blood glucose levels and significant weight loss, GLP-1s also provide cardiovascular benefits. They are, however, among the more expensive options due to the lack of generic alternatives for most GLP-1s.
- DPP-4 Inhibitors (e.g., Januvia): These drugs offer moderate glucose control and are weight-neutral with a low risk of hypoglycemia, suitable for patients who prioritize minimal side effects over more aggressive glucose reduction.
- Thiazolidinediones (e.g., pioglitazone): Although effective in reducing blood glucose, TZDs can cause weight gain and may exacerbate heart failure, limiting their use in patients with existing heart complications. They are available as generics, making them cost-effective options.
- Sulfonylureas (e.g., glyburide, glipizide): While effective in lowering blood sugar, Sulfonylureas can cause weight gain and significant hypoglycemia, posing a risk for cardiovascular events. They are, however, very inexpensive due to their generic status.
- Insulins (e.g., Humulin, Novolin, Humalog, Novolog): Insulin therapy is crucial for many, particularly those with type 1 diabetes or those who are severely insulin resistant. Although effective, insulin use requires careful management to avoid hypoglycemia and weight gain. Recent price reductions under the Inflation Reduction Act have enhanced affordability of some insulin products.
The Landscape of Diabetes Prescriptions: A Significant Shift Towards Newer Drug Classes
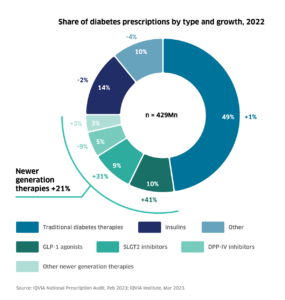
The chart below indicates a strategic shift towards more comprehensive diabetes management approaches, focusing on drugs that offer multi-faceted benefits beyond mere blood glucose control.
- SGLT-2 inhibitors experienced a 31% increase in prescription share
- GLP-1 receptor agonists saw a 41% rise, likely due to their strong impact on weight loss and cardiovascular outco
mes, despite their high cost. - Insulins saw a slight decrease of 2%, reflecting the broadening of options available for glucose control that may offer additional benefits with less risk of hypoglycemia.
Strategic Considerations for Drug Selection
Selecting the right drug involves balancing efficacy with potential side effects, following ADA guidelines and considering individual patient profiles, such as:
- Comorbidities: Cardiovascular and renal diseases prevalent in diabetics necessitate medications that cater to these complications alongside glucose control.
- Cost-Effectiveness: With the introduction of generics and price changes due to legislative actions, cost considerations are as crucial as clinical benefits.
- Patient Preferences and Tolerability: Medication adherence can be significantly impacted by the side effects profile and the complexity of the treatment regimen.
In managing diabetes effectively within a healthcare plan, it is vital to consider a broad spectrum of available medications, assessing each for its clinical and economic benefits. For brokers and employer groups, understanding these aspects enables informed decision-making that optimizes both healthcare outcomes and financial efficiency, ensuring that patients receive the best possible care without undue financial burden.
Interested in learning how AlignRx can help your groups manage spending on diabetes drugs? Reach out to your account manager today!
Sources:
References:
- Einarson TR, Acs A, Ludwig C, Panton UH. Prevalence of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes: a systematic literature review of scientific evidence from across the world in 2007-2017. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018 Jun 8;17(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12933-018-0728-6. PMID: 29884191; PMCID: PMC5994068.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Prevalence of overweight and obesity among adults with diagnosed diabetes–United States, 1988-1994 and 1999-2002. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2004 Nov 19;53(45):1066-8. PMID: 15549021.
- Cameron NA, Petito LC, McCabe M, Allen NB, O’Brien MJ, Carnethon MR, Khan SS. Quantifying the Sex-Race/Ethnicity-Specific Burden of Obesity on Incident Diabetes Mellitus in the United States, 2001 to 2016: MESA and NHANES. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Feb 16;10(4):e018799. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.018799. Epub 2021 Feb 10. PMID: 33563002; PMCID: PMC7955335.
- Feng XS, Farej R, Dean BB, Xia F, Gaiser A, Kong SX, Elliott J, Lindemann S, Singh R. CKD Prevalence Among Patients With and Without Type 2 Diabetes: Regional Differences in the United States. Kidney Med. 2021 Nov 3;4(1):100385. doi: 10.1016/j.xkme.2021.09.003. PMID: 35072048; PMCID: PMC8767132.
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Heart Failure: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association and the Heart Failure Society of America. Circulation 2019;Jun 6:[Epub ahead of print]

